Recombinant Human Solute carrier family 23 member 2 (SLC23A2), partial
-
中文名稱:人SLC23A2重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP866221HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人SLC23A2重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP866221HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人SLC23A2重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP866221HU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人SLC23A2重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP866221HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人SLC23A2重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP866221HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:SLC23A2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:SLC23A2; KIAA0238; NBTL1; SLC23A1; SVCT2; YSPL2; Solute carrier family 23 member 2; Na(+)/L-ascorbic acid transporter 2; Nucleobase transporter-like 1 protein; Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2; hSVCT2; Yolk sac permease-like molecule 2
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Sodium/ascorbate cotransporter. Mediates electrogenic uptake of vitamin C, with a stoichiometry of 2 Na(+) for each ascorbate.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- enhanced expression of the high affinity ascorbic acid transporter SVCT2, which tightly regulates intracellular ascorbic acid concentrations. PMID: 26646539
- mutant KRAS can be bypassed by L-ascorbic acid in an SVCT-2-dependent manner. Furthermore, SVCT-2 in mutant KRAS colon cancer may act as a potent marker for potentiating L-ascorbic acid co-treatment with cetuximab. PMID: 27012422
- These data suggest that both fruit intake and genetic marker in SLC23A2 may play an independent role in chronic lymphocytic leukemia biology. PMID: 26838684
- Ascorbic acid kills cholangiocarcinoma cells via DNA damage, ATP depletion, and inhibition of mTOR pathway in a SVCT-2 dependent manner. PMID: 28385602
- Our findings show, for the first time, that transporters of the water-soluble vitamin ascorbic acid (i.e., the vitamin C transporters SVCT-1 and SVCT-2) are differentially expressed along the length of the intestinal tract and that the pattern of expression is mediated, at least in part, by transcriptional and epigenetic mechanism(s) affecting both Slc23a1 and Slc23a2 genes. PMID: 27932501
- In title. PMID: 26188149
- Significant methylation changes in the SLC23A2 and NCOR2 regulatory regions. PMID: 25821969
- Vitamin C supplementation significantly increases skeletal muscle SVCT2 protein expression. PMID: 25242204
- ascorbic acid uptake mechanism, kinetics, and regulation by sodium dependent vitamin C transporter (SVCT2) in MDA-MB231, T47D and ZR-75-1 cells. PMID: 25102111
- Together, these data clarify previous inconsistencies in the literature andimplicate SVCT2 as the pericyte ascorbate transporter. PMID: 25645015
- The functional expression of SVCT2 was detected in HEK293 cells.The kinetic analysis suggested that an ascorbate-dependent mechanism accounts for targeted SVCT2 expression in the developing kidney during medullary epithelial cell differentiation. PMID: 22990596
- We propose that the mitochondrial localization of SVCT2 is a property shared across cells, tissues, and species. PMID: 24594434
- Demonstrate that the expression of SVCT2 transporter is significantly down-regulated in human grade 3 osteoarthritic tissues. PMID: 24401033
- polymorphisms in SLC23A1/2 genes influenced ascorbate concentration in aqueous humor and lens nucleus. PMID: 24815519
- Genetic variation in the sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 may have a role in acute coronary syndrome in women PMID: 23990905
- Data show that the mRNA level of svct2 was approximately 600- to 900-fold higher than that of svct1 indicating SVCT2 is a main isoform in fibroblast OUMS-36 cells, and no significant difference in svct2 mRNA and protein between young and old cells. PMID: 23613229
- Low SVCT2 transporter is associated with Type I diabetes. PMID: 23999113
- Data suggest that N-terminal and C-terminal sorting signals interact, directly or indirectly, within each gene family (here, SVCT1 and SVCT2) in basolateral targeting of transmembrane proteins to basolateral cell membrane. PMID: 23837633
- confirmed the association between rs1279683 (SLC23A2) and primary open-angle glaucoma PMID: 23401652
- The novel demonstration of SVCT2-dependent mitochondrial transport of ascorbic acid. PMID: 23288661
- glutathione depletion failed to affect ascorbic acid transport, and SVCT1 and SVCT2 expression in hepatoma cells. Therefore, our data indicate an essential role for glutathione in controlling vitamin C metabolism in rat hepatocytes and rat hepatoma cells PMID: 22348976
- The rs1279683 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in SLC23A2 was significantly associated with lower plasma concentrations of vitamin C and with higher risk of primary open-angle glaucoma in GG subjects. PMID: 22171153
- In patients with hepatocellular cholestasis, primary biliary cirrhosis, haemochromatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, using real-time RT-PCR, an enhanced hepatic expression of both SLC23A1 and SLC23A2 was found. PMID: 21733302
- Thus CpG methylation at the upstream USF-binding site functions in establishing and maintaining cell-specific transcription from the CpG-poor SVCT2 exon 1a promoter. PMID: 21770893
- Differential occupancy of transcription factors on the GC-rich consensus sequences in the sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter (SVCT2) exon 1b promoter contributes to the regulation of cell and tissue expression of SVCT2. PMID: 21335086
- hSVCT1 and 2 promoters establish that ascorbic acid uptake by human liver epithelial cells is adaptively regulated and show that transcriptional mechanisms via HNF-1 in the hSVCT1 promoter may, in part, be involved in this regulation. PMID: 20471816
- Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 19170196
- both NH(2)- and COOH-terminal sequences are essential for proper localization of hSVCT2, cell surface delivery is dependent on intact microtubules, and peripheral microfilaments regulate insertion and retrieval of hSVCT2 into the plasma membrane PMID: 19926816
- These findings suggest a mechanism of ascorbic acid uptake regulation whereby an alternative sodium-ascorbate cotransporter 2 (SVCT2) gene product inhibits transport through the two known ascorbic acid transporters. PMID: 15060139
- Functionally expressed in human endothelial cells and negatively regulated by inflammatory cytokines. May provide new insight into treatment of cardiovascular diseases with ascorbic acid. PMID: 15340249
- SVCT2 mediates the secondary active and concentrative transport of ascorbic acid in human chondrocytes PMID: 15921655
- Functionally, SVCT1 expression led to more transport activity from the apical membrane, while SVCT2 expression only increased the uptake under the condition when basolateral membrane was exposed. PMID: 15993839
- Findings link genetic variants in the vitamin C transporter gene SLC23A2 to spontaneous preterm birth. PMID: 16357110
- The promoter functionality of the two genomic regions of the hSVCT2 upstream of these alternative first exons in human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells was tested. PMID: 16380174
- SVCT2 may switch between a number of states with characteristic properties, including an inactive conformation in the absence of Ca(2+)/Mg(2+) PMID: 17012227
- SVCT2 mRNA expression in human first-trimester chorionic villi but not in term placental tissue. PMID: 17092984
- SVCT2 expression can be regulated at the translational level by ascorbic acid and the redox state. PMID: 17291984
- SVCT1 is responsible for epidermal ascorbic acid supply, whereas SVCT2 mainly facilitates ascorbic acid transport in the dermal compartment PMID: 17664139
- The results suggest that uncharged His109 of hSVCT2, directly or indirectly, contributes to substrate binding through the hydrogen bond. PMID: 18247577
- all three proximal tubule segments expressed the transporter but the S3 segment had the highest expression; Ascorbic acid transport in these cells was regulated by a single kinetic component that depended on the sodium concentration, pH and temperature PMID: 18614995
- N-Glycosylation is therefore essential for SVCT2 functionality. PMID: 18619416
- estrogen receptor 1, vitamin C receptors SLC23A1 and SLC23A2, and matrix metalloproteinase MMP3 and MMP9 are associated with susceptibility to lymphoma PMID: 18636124
- For SLC23A2, overall, there was no colorectal adenoma association with haplotypes, but two SNPs located in intron 8 and exon 11 could be associated (odds ratio = 0.49, 95% confidence interval = 0.25-0.95 for haplotype G-C vs. haplotype C-C). PMID: 18791929
- hSVCT2 protein and mRNA are expressed at higher levels in HepG2 cells and native human liver, and the cloned hSVCT2 promoter has more activity in HepG2 cells. PMID: 18845575
- transports Vitamin C, a vital antioxidant, into the brain PMID: 19162177
- These results collectively suggested a default apical targeting of SVCT, which is consistent with the evolution-based prediction. PMID: 19216494
- increased expression during macrophage differentiation PMID: 19232538
- common variants in SLC23A2, a gene that directly regulates active transport of ascorbic acid, can impact gastric cancer risk PMID: 19243932
- SLC23A2 genetic variation alters HPV16-associated HNSCC while also highlighting the important role of citrus exposure in this disease. PMID: 19346260
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Xanthine/uracil permease family, Nucleobase:cation symporter-2 (NCS2) (TC 2.A.40) subfamily
-
組織特異性:Ubiquitous.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
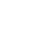
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
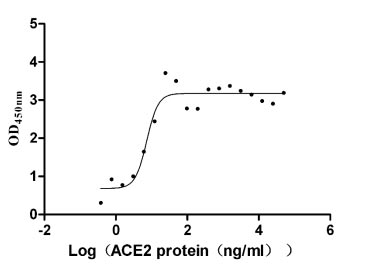
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
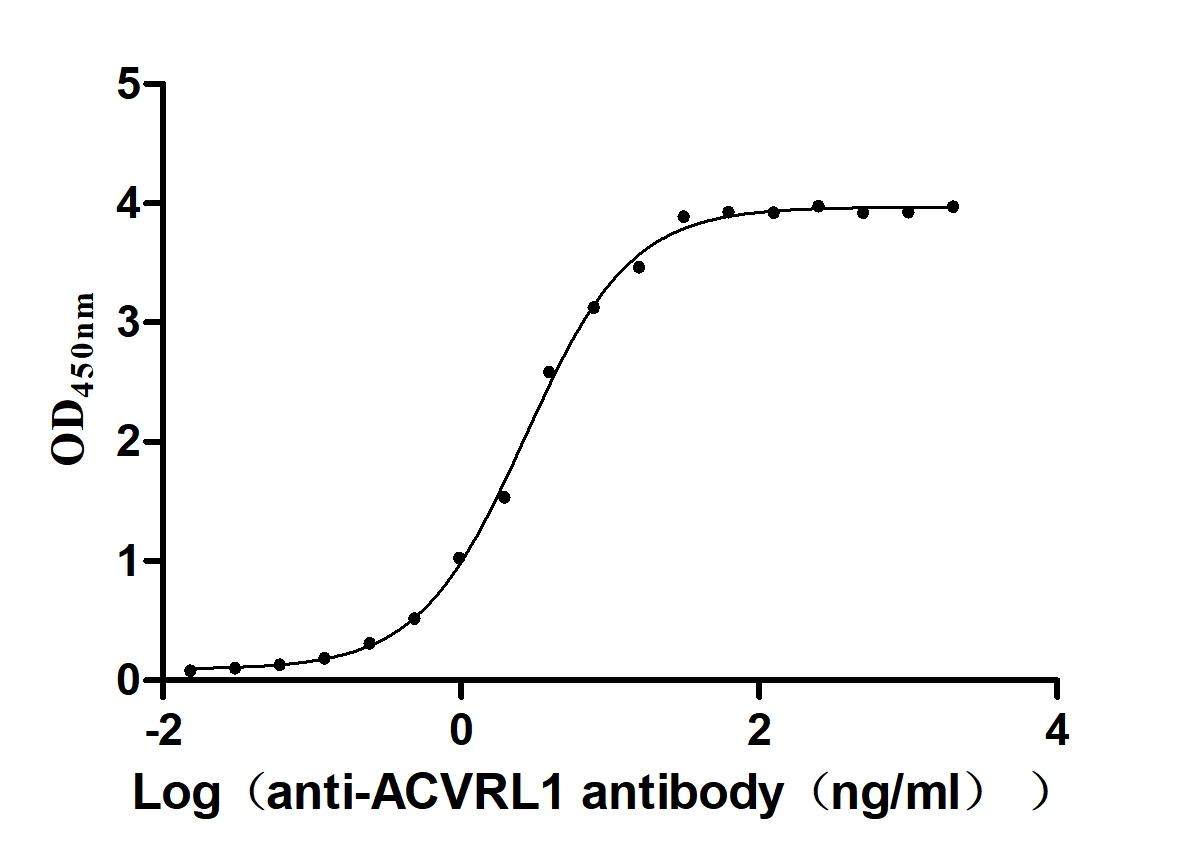
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
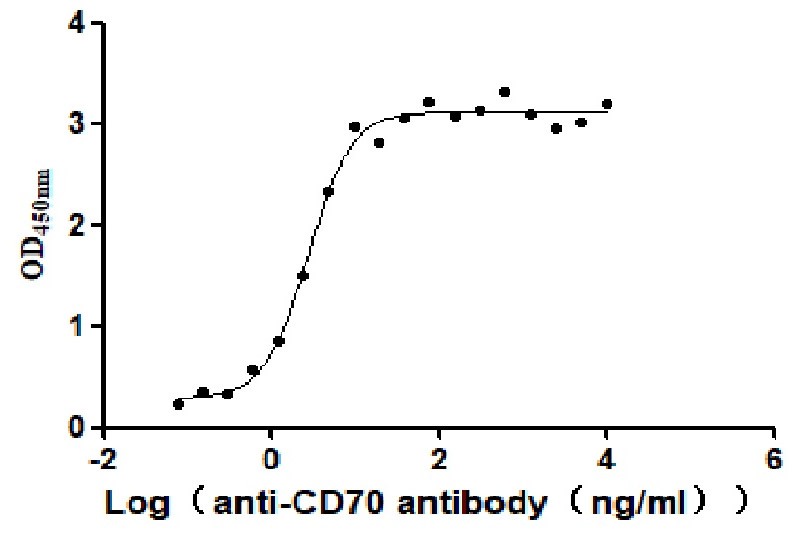
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
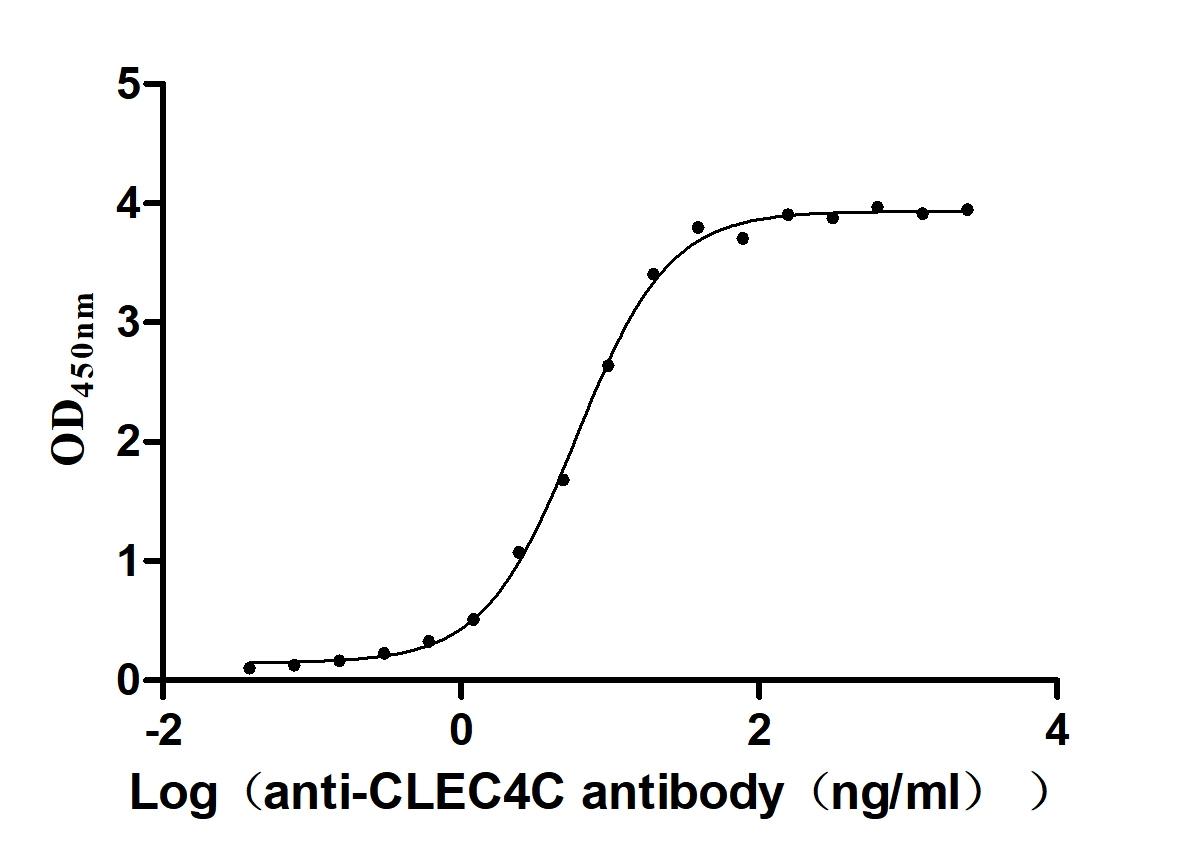
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
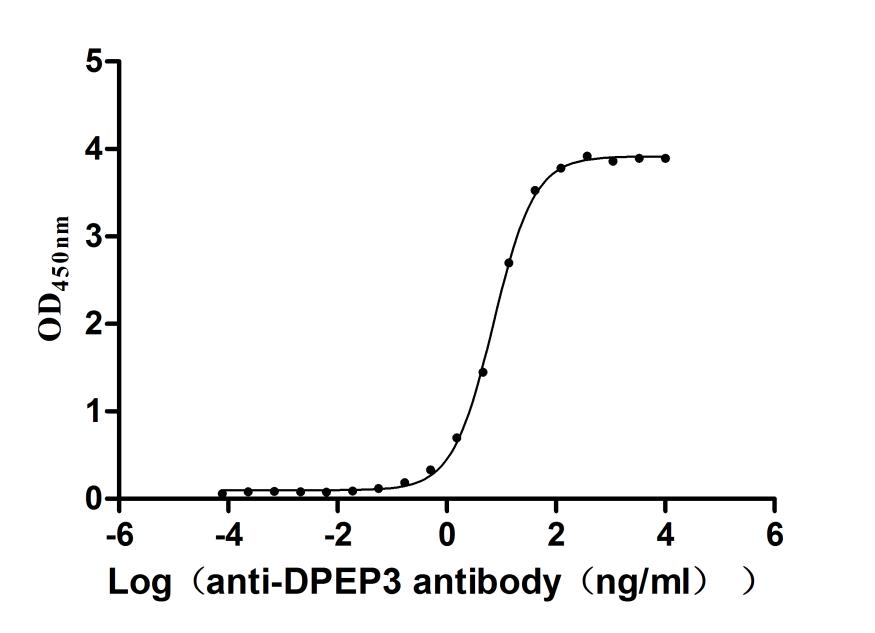
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)