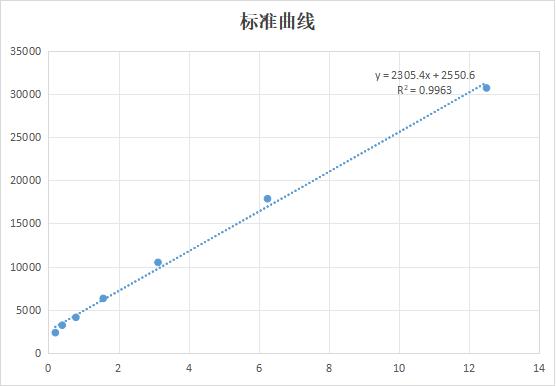
Recombinant Rat Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5 (Npy5r), partial
-
中文名稱:大鼠Npy5r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP714347RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Npy5r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP714347RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Npy5r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP714347RA1-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Npy5r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP714347RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Npy5r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP714347RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Npy5r; Npyr5; Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5; NPY5-R; NPY-Y5 receptor; NPYY5-R; Y5 receptor
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Receptor for neuropeptide Y and peptide YY. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that inhibit adenylate cyclase activity. Seems to be associated with food intake. Could be involved in feeding disorders.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- NPY and agonists of Y2R and Y5R may be neuroprotective against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal cell death in primary cortical cell cultures after delayed treatment. A Y2R agonist not only diminished transient cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury, but also improved functional outcome after delayed treatment. Y5 and especially Y2 receptors may be promising targets for neuroprotection against ischemic damage PMID: 28057538
- long-term over-expression of NPY in paraventricular nucleus contributes to the establishment of adipose tissue insulin resistance, at least partly via the Y5 receptor PMID: 25993471
- Our results showed the altered expression of NPY, Y1R and Y2R but not Y5R in hippocampus and temporal lobe cortex of tremor rat brain. PMID: 24444822
- Y5R does no tparticipate in the anorectic response to phenylpropanolamine. PMID: 23179670
- results suggest that while signals mediated through NPY Y1 receptors play a modest role in reinstatement, activation of Y5 receptors has a critical function in food deprivation-induced reinstatement of heroin-seeking behavior. PMID: 21629996
- the inhibition of central Y5 neurotransmission resulted in activation of thyroid axis during fasting suggesting that NPY-Y5 receptors contribute to fasting-induced TSH and TH suppression PMID: 21771616
- NPY and Y5R expression increased by more than 130-fold and decreased by 28-fold, respectively, in old bone marrow cells as compared to young bone marrow cells. PMID: 21595512
- via a specific Y-1R/Y-5R interplay, NPY acts as a neuroimmune co-transmitter in vivo. PMID: 12417430
- data suggest that over activity of the neuropeptide Y, neuropeptide Y-1 receptor, and neuropeptide Y-5 receptor gene expression may contribute to the development of obesity in OM rats PMID: 12429884
- data confirm the importance of both neuropeptide Y1 and Y5 receptors in the neuropeptide Y-mediated increase in food consumption and demonstrate that both receptors can mediate inhibitory effects of neuropeptide Y on the hypothalamo-pituitary-thyroid axis PMID: 12446577
- Comparative mapping of Y1 and Y5 receptor subtypes within cell bodies and nerve fibers in the brain which, together with physiological and electrophysiological studies, provide a better understanding of NPY neural circuitries. PMID: 12900925
- decreased expression and number of Y(5) receptors in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus cannot explain the attenuated responsiveness of the senescent rats to exogenous neuropeptide Y PMID: 15044185
- we investigated the regulation of BDNF and NPY mRNA and Y1-, Y2-, and Y5-like receptor binding in the hippocampus of vehicle-pretreated, partially and fully amygdala-kindled rats and corresponding levetiracetam-pretreated rats (40 mg/kg i.p.). PMID: 15123022
- data reveal an NPY Y1 and Y2/Y5 receptor interaction in NPY-induced modulation of macrophage functions related to inflammation PMID: 15544855
- Y5 receptors mediate inhibitory effects of NPY in kindling and display anticonvulsant rather then antiepileptogenic effects upon agonist stimulation PMID: 15582717
- Results describe the distribution of neuropeptide Y Y5 receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. PMID: 16954600
- Selective stimulation of Y(5) receptor provokes activation of the HPA axis and its downstream pathway is chiefly composed of both CRF (primary regulator) and AVP (subordinate to the former) with distinct relative contribution. PMID: 17363455
- These results suggest that in addition to regulating feeding behaviour, the Y5 receptor subtype may have previously unrecognised roles in the control of nesting behaviour during lactation with subsequent effects on litter growth rates. PMID: 19419662
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
組織特異性:Brain; hypothalamus.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
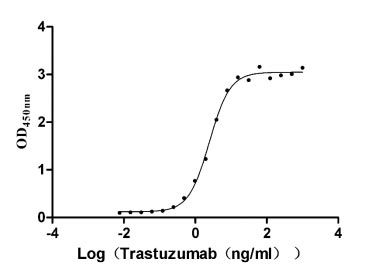
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
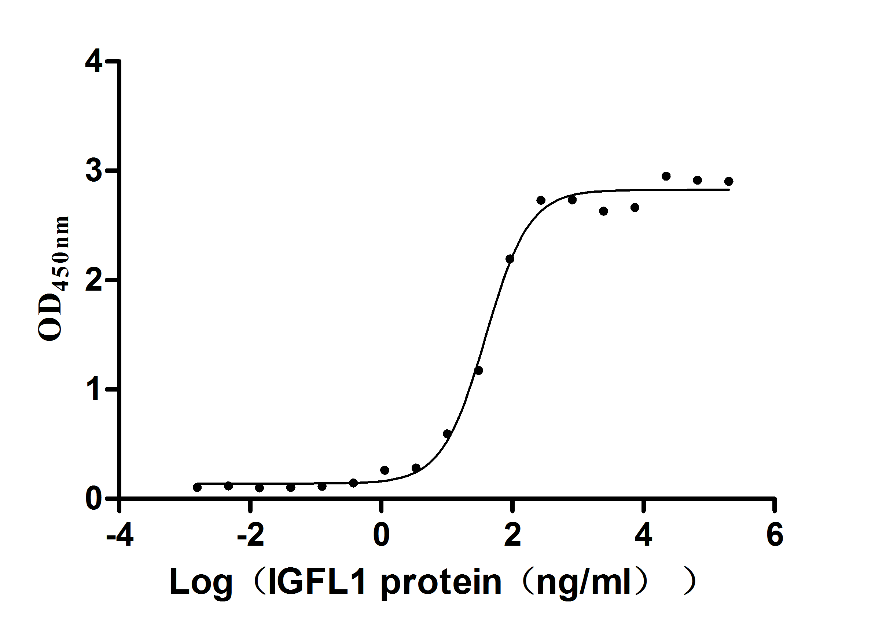
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
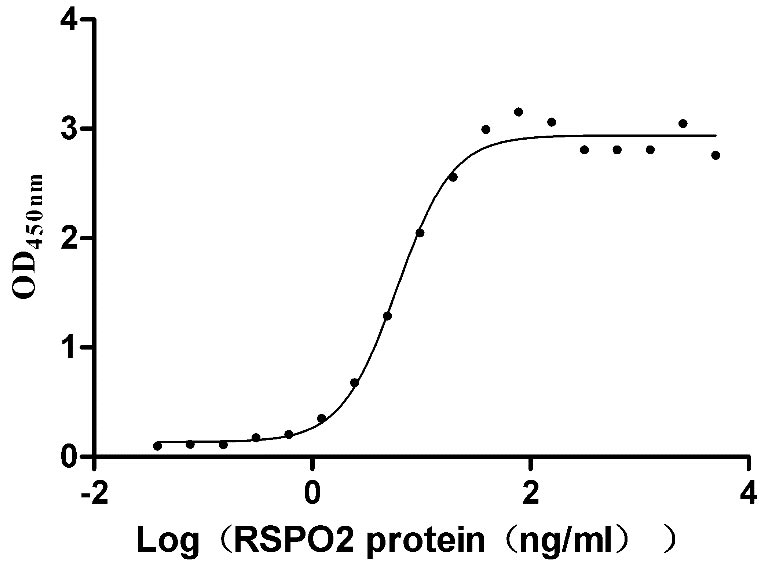
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 (ZNRF3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
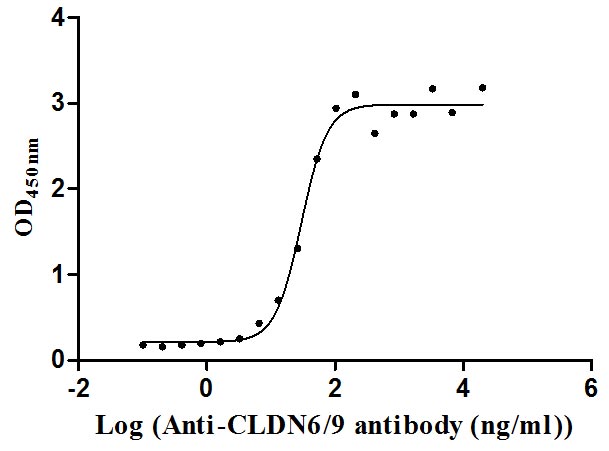
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(PLAU) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)