Recombinant Mouse Melanocortin receptor 4 (Mc4r), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mc4r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP013561MO1
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mc4r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP013561MO1
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mc4r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP013561MO1-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mc4r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP013561MO1
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mc4r重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP013561MO1
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Mc4r; Melanocortin receptor 4; MC4-R
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Receptor specific to the heptapeptide core common to adrenocorticotropic hormone and alpha-, beta-, and gamma-MSH. Plays a central role in energy homeostasis and somatic growth. This receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase (cAMP).
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Mc4r knockout offspring showed higher body, liver and adipose tissue weights; and mild hepatic steatosis PMID: 28930194
- vertebrate limb regeneration with Mc4r-mediated energy homeostasis and provide a new avenue for understanding Mc4r signaling in the peripheral organs PMID: 30130530
- Together this study identifies MC4R deletion as a novel and potentially clinically important cause of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. PMID: 28829041
- Data suggest that central melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4-R) and tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) are involved in the efferent neuronal control of the kidneys. PMID: 27626491
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest that expression of Mc4r in Sim1 neurons of arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus, paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, and amygdala is involved in sexual function; here, expression of Mc4r only on Sim1 neurons reverses sexual deficits seen in Mc4r null mice. (Mc4r = melanocortin 4 receptor; Sim1 = single-minded homolog 1) PMID: 29059347
- disruption of this hippocampal POMC/MC4R circuit might contribute to synaptic dysfunction observed in Alzheimer's disease. PMID: 27829153
- Study shows that melanocortin 4 receptor constitutive activity chronically inhibits specific subtypes of neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels. PMID: 28093215
- Loss of MC4R is associated with hepatic steatosis. PMID: 28003536
- The data suggest that lipid stress disrupts steps of endocytosis following MC4R localization to clathrin-coated sites and exclusion of the receptor from the extracellular medium. PMID: 28878020
- Confirmation of the impairment of GH-IGF-1 release in hyperphagic MC4R KO mice suggests a role for insulin in regulating both the release of GH, but also in mediating growth during periods of physiologically suppressed GH-IGF-1 levels PMID: 27558671
- Loss of Mc4r expression is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 28207798
- results indicate that the MC4R is not required for estrogen's effects on metabolic and reproductive functions PMID: 28403939
- Mc4r receptor expression in the cuneiform nucleus is involved in modulation of opioidergic signaling. PMID: 26489618
- Together, these results suggest that alpha-MSH alleviates Dex-induced damages to cultured osteoblasts through activating MC4R-SphK1 signaling. PMID: 26631960
- Our findings support the hypothesis that MC4R signaling in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus may involve in the modulation of midbrain dopamine systems. PMID: 25973101
- These results indicate that intact CNS MC4R signaling is necessary for leptin to exert its chronic antidiabetic, anorexic, and cardiovascular actions. PMID: 25717164
- Mc4r signaling has a protective role in minimizing glucose fluctuations due to circadian rhythms and environmental light cues, a previously undiscovered connection between circadian biology and glucose metabolism mediated through the melanocortin system. PMID: 25730108
- MC4R specifically inhibited the presynaptic N-type channel subtype, and this inhibition may be important for the effects of melanocortin in the central subdivision of the amygdala PMID: 24943127
- Coupling of MC4R to Kir7.1 may explain unusual aspects of the control of energy homeostasis by melanocortin signalling, including the gene dosage effect of MC4R and the sustained effects of AgRP on food intake. PMID: 25600267
- The MC4R-expressing neurons regulating feeding are SIM1(+), located in the paraventricular hypothalamus, glutamatergic and not GABAergic, and do not express oxytocin, corticotropin-releasing hormone, vasopressin, or prodynorphin. PMID: 25157144
- These findings highlight an essential, and to our knowledge previously unknown, role for Ca(2+) signaling in the MC4R pathway that leads to satiety, and a novel non-redundant role for NCKX4-mediated Ca(2+) extrusion in controlling MC4R signaling PMID: 25096581
- Posttranscriptional decrease of MC4R protein lowers the response to alpha-MSH in hypothalamic neurons exposed to even a mild level of lipid stress. PMID: 24506538
- MC4R signaling in motor cortex- periaqueductal gray-spinal cord neural pathway may modulate the activity of sympathetic outflow sensitive to nociceptive signals. PMID: 24586817
- Our findings support the hypothesis that MC4R signaling in RVM may modulate the activity of serotonergic sympathetic outflow sensitive to nociceptive signals, and that MC4R signaling in RVM may contribute to the descending modulation of nociception. PMID: 23592129
- Deletion of Mc4r genes in both sympathetic and parasympathetic cholinergic neurons impaired glucose homeostasis PMID: 24908101
- MC4R-expressing dorsal motor nucleus neurons may participate in the regulation of glucose/insulin homeostasis through their projections to the intrapancreatic ganglia PMID: 24028856
- MC4R signaling in D1R neurons regulates food intake and development of locomotor sensitization to cocaine. PMID: 23786641
- Exposure of MC4R to agonist in the endoplasmic reticulum stabilizes an active conformation of the receptor that does not desensitize. PMID: 24248383
- The results of this study provided evidence the role of MC4-R expressed by neurons innervating the PVH that are also sensitive to reproductive cues. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PMID: 23485805
- MC4Rs in Pomc neurons are important for regulation of energy balance but do not have major role in regulation cardiovascular functions. PMID: 23842677
- our novel findings show that activation of MC4-Rs in the brainstem modulates gastric activity, which may have physiological relevance for food intake and gastric function PMID: 23946387
- Both constitutive and induced genetic deletion of the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) gene normalizes compulsive grooming and striatal electrophysiologic impairments in SAPAP3-null mice PMID: 23754400
- MC4Rs in autonomic neurons mediate beneficial effects of roux-en-Y gastric bypass, including weight-independent improved glucose homeostasis, in mice and humans. PMID: 23159449
- our findings demonstrate variegated MC4R expression in different classes of vagal and spinal primary afferent neurons PMID: 22592759
- Deletion of MC4Rs in cholinergic neurons resulted in elevated levels of insulin. Furthermore, re-expression of MC4Rs specifically in cholinergic neurons (including sympathetic preganglionic neurons) restores obesity-associated hypertension in MC4R null mice. PMID: 23374353
- MC4R in the hippocampus plays a critical role in the regulation of structural and functional plasticity PMID: 23303927
- MC4RKO mice display increased lean body mas PMID: 22848742
- heparanase acts as a negative modulator of AgRP signaling at MC4R, through cleavage of heparan sulfate chains presumably linked to syndecan-3 PMID: 22479599
- MC4R(-/-) mice lost substantially less weight after surgery than wild-type animals, indicating that MC4R signaling is necessary for the weight loss effects of gastric bypass in this model. PMID: 22492873
- chronic stress in mice decreases the strength of excitatory synapses on D1 dopamine receptor-expressing nucleus accumbens medium spiny neurons owing to activation of the melanocortin 4 receptor PMID: 22785313
- data identify a novel requirement for MC4R signaling in procedural memory learning. PMID: 22342812
- MC4R and NPY are required for activation of hepatic pathways that metabolize T(4) during the fasting response. PMID: 22100407
- Melanocortin 4 receptor is a transcriptional target of nescient helix-loop-helix-2 PMID: 21664420
- the md and mg mutations rescue the A(y) phenotypes by a primarily cAMP-independent mechanism promoting trafficking of MC4R and likely MC1R away from the lysosome toward the cell surface. PMID: 21460229
- Analysis of the microstructure of feeding behavior in response to dietary fat in the MC4R(-/-) and MC4R(+/-) mice indicates that the high-fat hyperphagia involves defective satiation and an increased rate of food intake. PMID: 21239438
- A long-term high-fat diet may have an effect on the methylation status of the Mc4r gene in mice. PMID: 20453306
- T(3) repression of Mc4r transcription ensures that the energy-saving effects of T(3) feedback on Trh are not overridden by MC4R activation of Trh PMID: 20160073
- Data suggest that MC4R signaling in vagal afferents may modulate the activity of fibers sensitive to satiety signals such as cholecystokinin, and that MC4R signaling in vagal efferents may contribute to the control of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. PMID: 19882715
- has a role in sexual function in mice PMID: 12172010
- MC4R deficiency primarily causes hyperphagia without hypometabolism: total body fat content of MC4r-/- animals on day 35 and MC4r+/- on day 56 significantly exceeds that of MC4r+/+ mice. PMID: 12644632
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
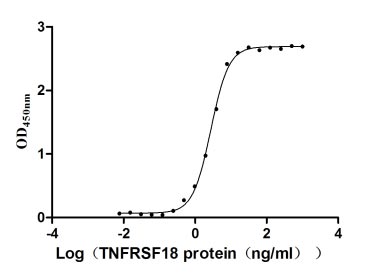
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
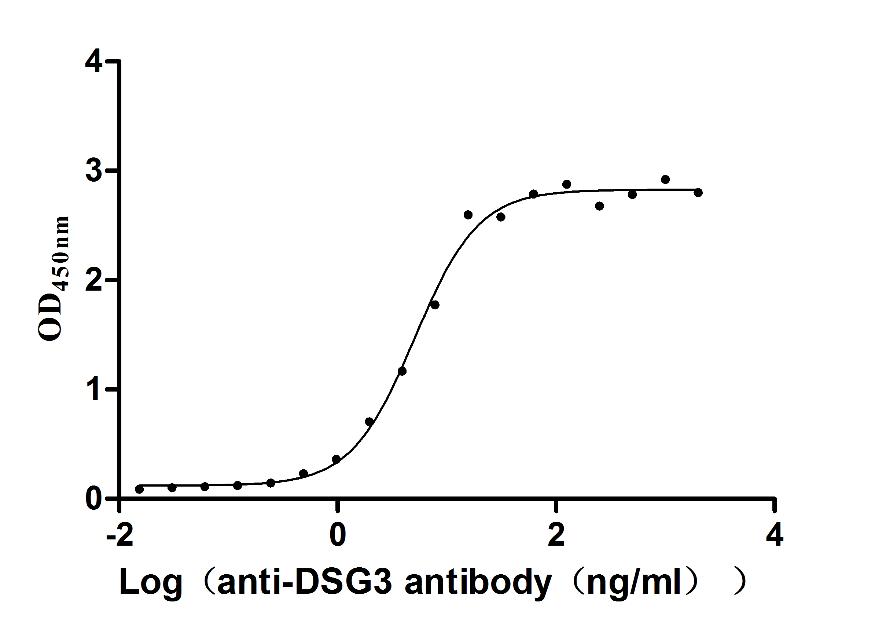
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
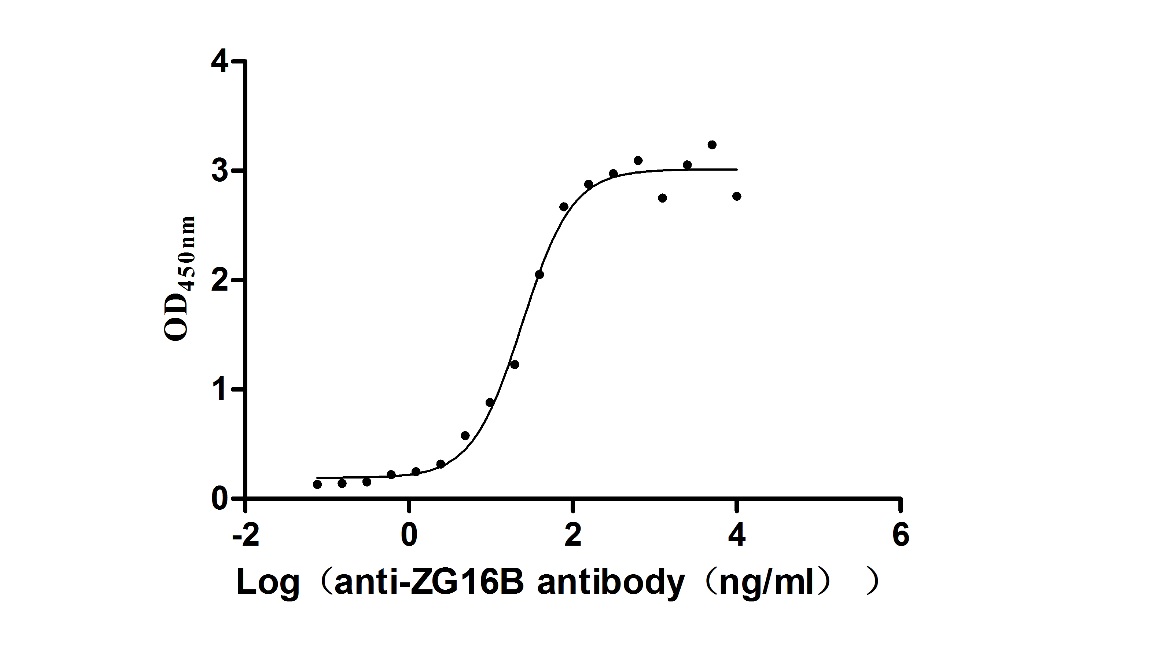
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
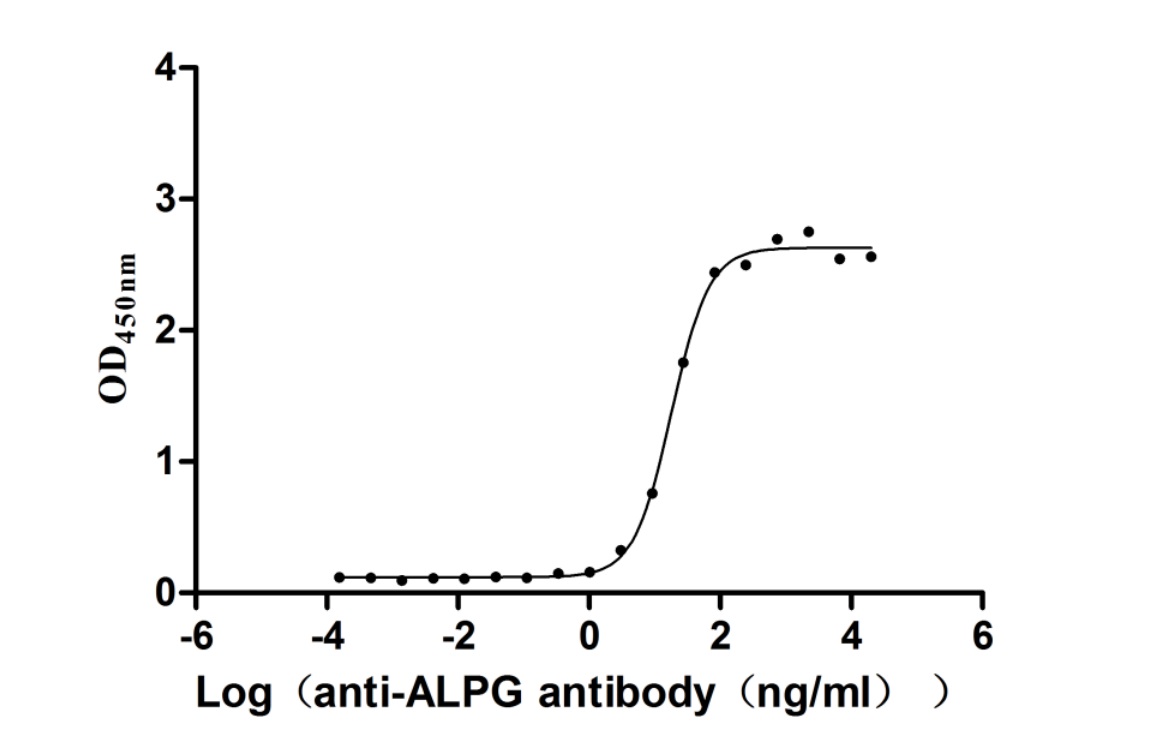
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
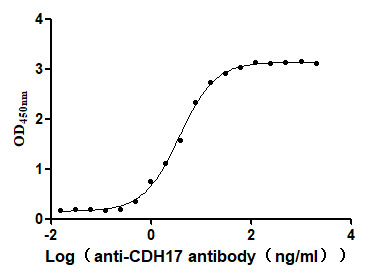
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
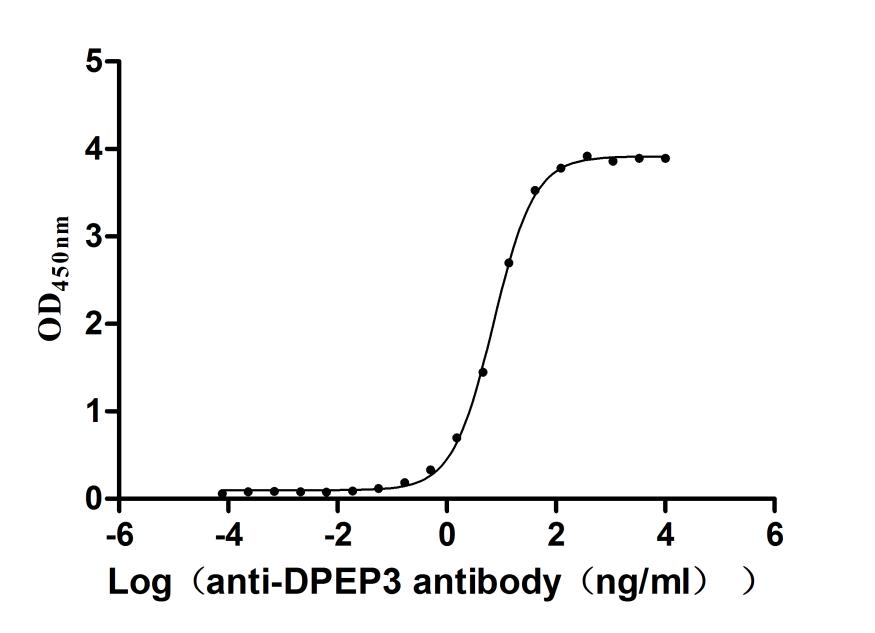
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-


-AC1.jpg)