Recombinant Human Protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP14 (PARP14), partial
-
中文名稱:人PARP14重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP677190HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PARP14重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP677190HU-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
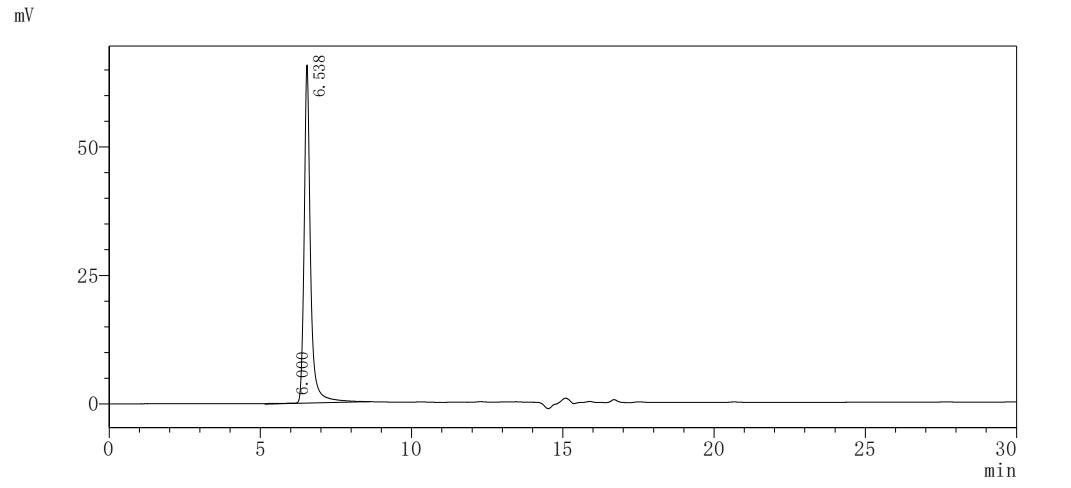
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PARP14
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 8; ARTD8; B aggressive lymphoma protein 2; BAL2; Collaborator of STAT6; KIAA1268; PAR14_HUMAN; PARP 14; PARP-14; PARP14; pART8; Poly (ADP ribose) polymerase family member 14; Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 14
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates mono-ADP-ribosylation of glutamate residues on target proteins. In contrast to PARP1 and PARP2, it is not able to mediate poly-ADP-ribosylation. Has been shown to catalyze the mono-ADP-ribosylation of STAT1 at 'Glu-657' and 'Glu-705', thus decreasing STAT1 phosphorylation which negatively regulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages in response to IFNG stimulation. However, the role of ADP-ribosylation in the prevention of STAT1 phosphorylation has been called into question and it has been suggested that the inhibition of phosphorylation may be the result of sumoylation of STAT1 'Lys-703'. Mono-ADP-ribosylates STAT6; enhancing STAT6-dependent transcription. In macrophages, positively regulates MRC1 expression in response to IL4 stimulation by promoting STAT6 phosphorylation. Mono-ADP-ribosylates PARP9.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- PARP9 and PARP14 regulate macrophage activation in macrophage cell lines treated with either IFNgamma or IL-4; PARP14 silencing induces pro-inflammatory genes and STAT1 phosphorylation in M(IFNgamma) cells, whereas it suppresses anti-inflammatory gene expression and STAT6 phosphorylation in M(IL-4) cells PMID: 27796300
- The PARP14-JNK1-PKM2 regulatory axis is an important determinant for the Warburg effect in tumour cells and provides a mechanistic link between apoptosis and metabolism. PMID: 26258887
- PARP14 interacts with the DNA replication machinery component PCNA and promotes replication of DNA lesions and common fragile sites. PMID: 25753673
- The present study further suggests that the combined targeted inhibition of STAT1, ARTD8, ARTD9 and/or DTX3L could increase the efficacy of chemotherapy or radiation treatment in prostate and other high-risk tumor types with an increased STAT1 signaling. PMID: 24886089
- PARP14 has a significant role in the development of allergic inflammation, and targeting PARP14, or even PARP activity in general, might be an effective therapy for allergic diseases including eosinophilic esophagitis. PMID: 24238647
- Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 14 (PARP14) is a novel effector of the JNK2-dependent pro-survival signal in multiple myeloma. PMID: 23045269
- loss of PARP14 protein is a feature of gastric and colorectal cancers with high microsatellite instability and these alterations might contribute to development of cancers with high microsatellite instability by deregulating PARP-mediated signaling PMID: 21333322
- BAL macro domains repress transcription when tethered to a promoter; BAL2 and BAL3, but not BAL1, exhibit PARP activity PMID: 16061477
- PARP enzymatic activity is associated with CoaSt6, and this function of CoaSt6 can append ADP-ribose to itself and p100 PMID: 17478423
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
組織特異性:Expressed in macrophages.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
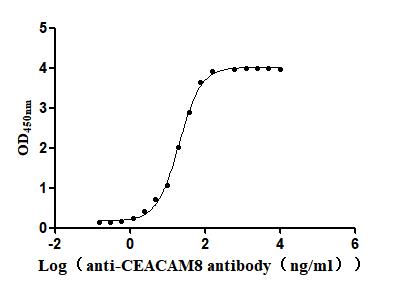
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)