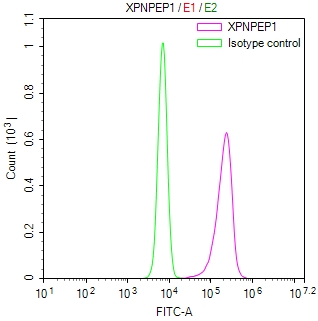
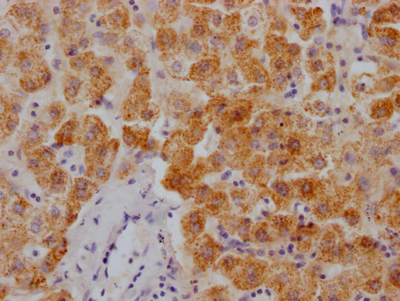
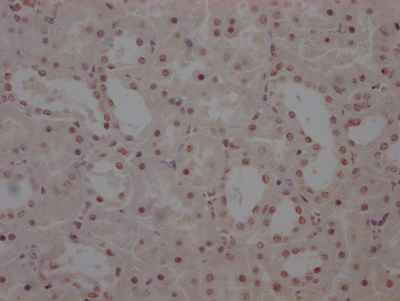
SGCE Antibody, Biotin conjugated
-
中文名稱:SGCE兔多克隆抗體, Biotin偶聯
-
貨號:CSB-PA021185LD01HU
-
規格:¥880
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) SGCE Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:SGCE
-
別名:SGCE; ESG; UNQ433/PRO840; Epsilon-sarcoglycan; Epsilon-SG
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Epsilon-sarcoglycan protein (8-126AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Biotin
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Component of the sarcoglycan complex, a subcomplex of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex which forms a link between the F-actin cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- The characterization of iPSC-derived cortical neurons with mutations in SGCE revealed that these cells are a suitable model mirroring the endogenous environment in the myoclonus-dystonia patient brain, especially, when focusing on concrete molecular aspects of the disease mechanism. PMID: 28155872
- A novel nonsense SGCE mutation was found in a Japanese family with myoclonus-dystonia. PMID: 28707723
- This study demonstrated that Psychiatric features are not likely to be related with the SGCE mutation itself but just bespeak disability in clinical MD syndrome regardless of the SGCE mutation. PMID: 28690014
- SGCE mutation can cause a broad range of clinical symptoms between and within families. We should consider MDS as a differential diagnosis for patients with paroxysmal walking abnormalities and/or myoclonic movements. PMID: 25868953
- Tata confirms that SGCE mutations are most commonly identified in Myoclonus dystonia syndrome patients with (1) age at onset PMID: 25209853
- found one patient with a novel heterozygous frameshift mutation in the DYT11 gene PMID: 25150291
- The co-occurrence of seizures and myoclonus-dystonia suggests that they are both due to the same underlying SGCE mutation PMID: 24297365
- A novel frameshift mutation of the SGCE gene in an Iranian family with Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome confirming the variability of the clinical symptoms caused by the same mutation within members of a family. PMID: 25034659
- In myoclonus-dystonia syndrome patients a substantial mutation in exon 3 of SGCE gene was found. PMID: 23561547
- The results of this study suggested performing gene dosage analysis by multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) to individuate large SGCE deletions that can be responsible for complex phenotypes. PMID: 23677909
- SGCE mutations are associated with a specific psychiatric phenotype consisting of compulsivity, anxiety and alcoholism in addition to the characteristic motor phenotype. PMID: 23365103
- Although reduced penetrance in DYT11-MD has been attributed to the maternal imprinting epsilon-sarcoglycan mutations, NM-DYT11 carriers showed significant metabolic abnormalities that are not explained by this genetic model. PMID: 23284065
- anxiety disorders and executive dysfunctions may be part of the phenotype of myoclonus-dystonia patients with a DYT11 mutation PMID: 22626943
- The results of this review confirmed the association of epsilon-sarcoglycan gene mutations with psychiatric disease and suggest a possible separation of the motor and psychiatric effects. PMID: 21713999
- This report presents a novel mutation in the SGCE gene causing myoclonus dystonia and extends the phenotype of myoclonus dystonia to also include alcohol-induced dystonia. PMID: 22026499
- Dystonia severity in twenty-five clinically affected DYT11 mutation carriers is strongly correlated with increased gray matter volume in bilateral putamina. PMID: 21219543
- This study demonistrated that Familial 7q21.3 microdeletion involving epsilon-sarcoglycan causing myoclonus dystonia, cognitive impairment, and psychosis. PMID: 21425342
- the mRNA expression level of SGCE were significantly up-regulated in tumorous liver tissues compared with corresponding nontumorous counterparts PMID: 21767414
- This study provides the first neurophysiological evidence of cerebellar dysfunction in DYT11 dystonia and supports a role of cerebellar dysfunction in the myoclonus-dystonia phenotype. PMID: 21386109
- Biased SGCE gene expression is based on parent of origin rather than on a strictly dichotomous maternal imprinting mechanism, consistent with clinical observations. PMID: 21320983
- loss of function of the brain-specific SGCE isoform underlies the exclusively neurological myoclonus-dystonia phenotype PMID: 21157498
- Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the internal pallidum proves to be safe and highly effective therapy in a homogeneous population of patients with myoclonus-dystonia due to genetically proved epsilon-sarcoglycan deficiency. PMID: 21220679
- This study identified three novel mutations of SGCE in the respective three myoclonus-dystonia syndrome families in Taiwan. PMID: 20800530
- MMP-7 and SGCE are distinctive molecular factors in sporadic colorectal cancers from the mutator phenotype pathway PMID: 20372795
- Evidence that paternal expression of the epsilon-sarcoglycan gene accounts for reduced penetrance in myoclonus-dystonia PMID: 12444570
- Physiology and surgical response for a 63-year-old woman who underwent deep brain stimulation for myoclonus dystonia related to a SGCE mutation. PMID: 19896264
- 33 month old girl & her twin brother presenting myoclonus on intentional tasks; family history was positive for paternal uncle, his 2 daughters & paternal great grandfather; sequencing revealed a novel nonsense mutation c.942C>A (p.Tyr314X) in exon 7. PMID: 19147379
- Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome: epsilon-sarcoglycan mutations and phenotype PMID: 12325078
- Myoclonus-dystonia is a movement disorder associated with mutations in the epsilon-sarcoglycan gene (SGCE) in most families and in the DRD2 and DYT1 genes in two single families. PMID: 12402271
- placental transcription from SGCE remained unchanged throughout pregnancy PMID: 12620933
- Severe myoclonus-dystonia syndrome characterized by obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, and anxiety was shown to be associated with a novel truncating mutation located within exon 4 of SGCE. PMID: 12707948
- Genetic analysis of a 5-generation Dutch family with inherited myoclonus-dystonia revealed a 1-bp insertion (885Tins)in exon 7 of the SGCE gene, resulting in frameshift and subsequent protein truncation at amino acid 297. PMID: 12821748
- We describe 3 children with a similar clinical picture of autosomal dominant M-D and an SGCE mutation in only one of them, suggesting that M-D is genetically heterogeneous. PMID: 14978685
- Mutatoins sarse not sassociaatd with sporadic Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. PMID: 15627203
- 3 new mutations were found in patients with essential myoclous or myoclonic dystonia:R372X, 564-576del, IVS3-3T>C. PMID: 15728306
- onset with both myoclonus and dystonia, and axial dystonia were detected significantly more often in the epsilon-sarcoplycan mutation carriers. PMID: 16534121
- Some Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome-associated mutations in SGCE impair trafficking of the mutant protein to the plasma membrane. PMID: 17200151
- a heterozygous point mutation in the epsilon-sarcoglycan gene, which leads to skipping of exon 5 in a family with myoclonus-dystonia syndrome complicated with severe depression PMID: 17230465
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder and alcohol dependence are associated with manifesting mutated SGCE. PMID: 17296918
- Our findings are not sufficient to conclude whether different SGCE mutations could lead to different phenoytpes of myoclonus-dystonia. PMID: 17394244
- Korean Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome family with a novel splicing mutation of the SGCE gene and a unique phenotype mimicking Moya-Moya disease. PMID: 17394247
- Autosomal dominant myoclonus-dystonia and Tourette syndrome in a family without linkage to the SGCE gene. PMID: 17702041
- Two additional patients carried a de novo SGCE nonsense mutation in exon 3 (R97X) and a novel SGCE missense mutation in exon 6 (G227V) in this study. PMID: 17702043
- Genomic deletion size at the epsilon-sarcoglycan locus determines the clinical phenotype in myoclonus-dystonia. PMID: 17898012
- intragenic deletions with SGCE and it highlights the need to include exonic copy number variation when performing mutational analysis of SGCE. PMID: 18098280
- Real-time PCR showed that ETOH significantly altered the expression of genes involved in cell adhesion. There was an increase in the expression of alpha and beta Laminins 1, beta Integrins 3 and 5, Secreted phosphoprotein1 and Sarcoglycan epsilon. PMID: 18162078
- Myoclonus-dystonia due to SGCE protein mutations is characterized by early onset myoclonic jerks, often associated with dystonia. PMID: 18175340
- Two heterozygous deletions of the entire SGCE gene and flanking DNA and a heterozygous deletion of exon 2 only were detected, accounting for 33% (3/9) of the mutations found. PMID: 18205193
- There was no association of the SCGE coding & flanking intronic region in OCD and/or GTS or CMT. The functional relevance of a newly found c.1314+172T>C 3'-untranslated region variant has yet to be determined. PMID: 18349702
- No muscle involvement in myoclonus-dystonia caused by epsilon-sarcoglycan gene mutations. PMID: 18355305
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Dystonia 11, myoclonic (DYT11)
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane, sarcolemma; Single-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell projection, dendrite. Golgi apparatus.
-
蛋白家族:Sarcoglycan alpha/epsilon family
-
組織特異性:Ubiquitous.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-