ATP2C1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:ATP2C1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA002339LA01HU
-
規格:¥440
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) ATP2C1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:ATP2C1
-
別名:1700121J11Rik antibody; AT2C1_HUMAN antibody; ATP dependent Ca(2+) pump PMR1 antibody; ATP-dependent Ca(2+) pump PMR1 antibody; ATP2C1 antibody; ATP2C1A antibody; ATPase 2C1 antibody; ATPase Ca(2+) sequestering antibody; ATPase Ca++ transporting type 2C member 1 antibody; AW061228 antibody; BCPM antibody; Calcium transporting ATPase type 2C member 1 antibody; Calcium-transporting ATPase type 2C member 1 antibody; D930003G21Rik antibody; HHD antibody; hSPCA1 antibody; HUSSY 28 antibody; KIAA1347 antibody; MGC58010 antibody; MGC93231 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216066 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216068 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216069 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216071 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216072 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216073 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216074 antibody; OTTHUMP00000216075 antibody; PMR1 antibody; PMR1; rat; homolog of antibody; PMR1L antibody; Secretory pathway Ca(2+) ATPase 1 antibody; Secretory pathway Ca(2+)-transporting ATPase antibody; Secretory pathway Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase 1 antibody; SPCA antibody; SPCA1 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Calcium-transporting ATPase type 2C member 1 protein (491-605AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
本頁面中的產品,ATP2C1 Antibody (CSB-PA002339LA01HU),的標記方式是Non-conjugated。對于ATP2C1 Antibody,我們還提供其他標記。見下表:
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
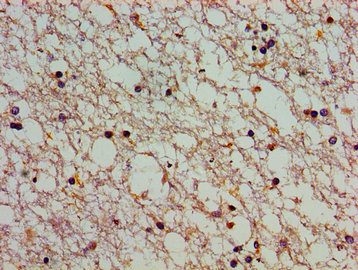
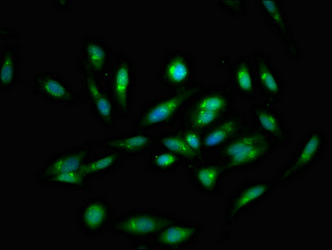
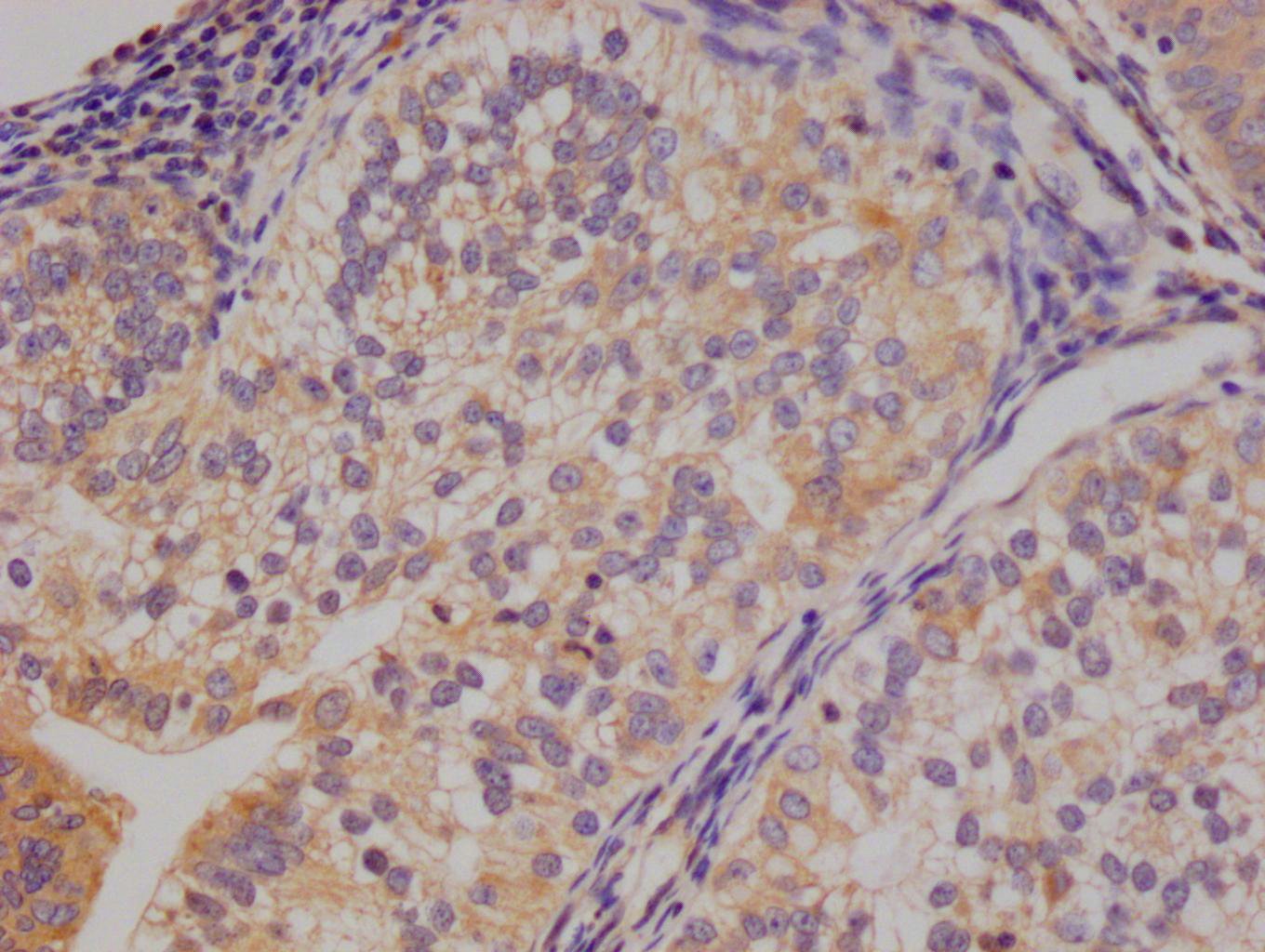
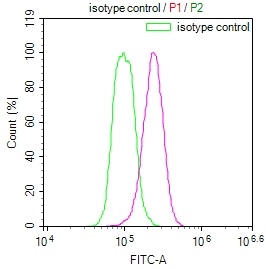
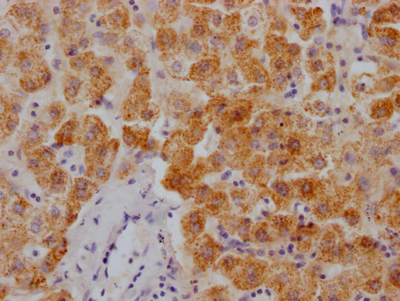
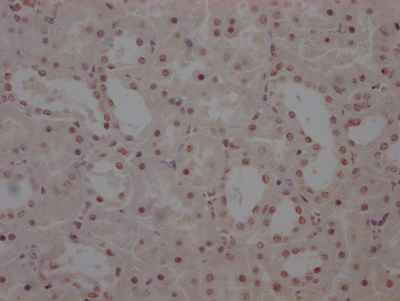
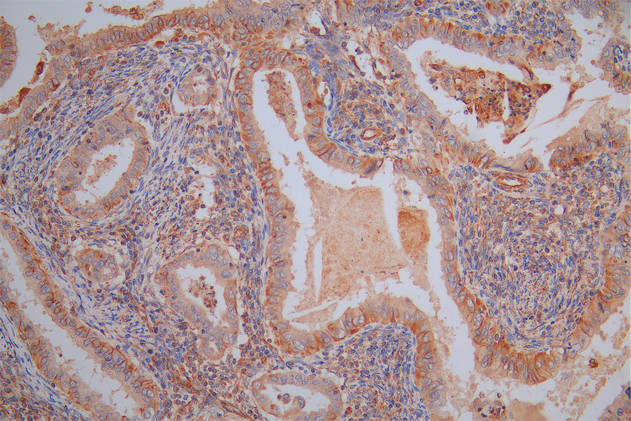
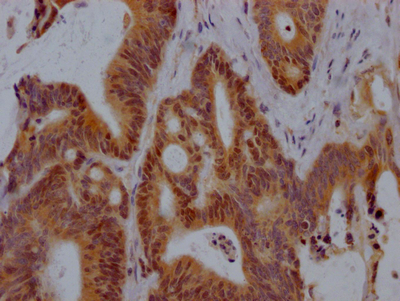
應用范圍:ELISA, IHC, IF
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 IF 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:ATP-driven pump that supplies the Golgi apparatus with Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) ions, both essential cofactors for processing and trafficking of newly synthesized proteins in the secretory pathway. Within a catalytic cycle, acquires Ca(2+) or Mn(2+) ions on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and delivers them to the lumenal side. The transfer of ions across the membrane is coupled to ATP hydrolysis and is associated with a transient phosphorylation that shifts the pump conformation from inward-facing to outward-facing state. Plays a primary role in the maintenance of Ca(2+) homeostasis in the trans-Golgi compartment with a functional impact on Golgi and post-Golgi protein sorting as well as a structural impact on cisternae morphology. Responsible for loading the Golgi stores with Ca(2+) ions in keratinocytes, contributing to keratinocyte differentiation and epidermis integrity. Participates in Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) ions uptake into the Golgi store of hippocampal neurons and regulates protein trafficking required for neural polarity. May also play a role in the maintenance of Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) homeostasis and signaling in the cytosol while preventing cytotoxicity.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- The calcium pump SPCA1 regulates proteases within the trans-Golgi network that require calcium for their activity and are critical for virus glycoprotein maturation. PMID: 29024641
- the functional coupling between SPCA1 and Orai1 increases cytosolic and intraluminal Ca(2+) levels, representing a novel mechanism of store-independent Ca(2+) entry that may be affected in Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 29555205
- We examined 2 familial and 2 sporadic cases of Hailey-Hailey Disease. Genomic DNA polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing of the ATP2C1 were performed from HHD patients, unaffected family members, and 200 healthy individuals.We detected 3 heterozygous mutations, including 2 novel frameshift mutations (c.819insA (273LfsX) and c.1264insTAGATGG (421LfsX)) and 1 recurrent nonsense mutation (c.115C>T (R39X)). PMID: 29104283
- results indicate that an ATP2C1/NOTCH1 axis might be critical for keratinocyte function and cutaneous homeostasis, suggesting a plausible model for the pathological features of Hailey-Hailey disease PMID: 27528123
- Studies indicate that Darier disease (DD) is caused by mutations in the ATP2A2 gene, whereas the ATP2C1 gene is associated with Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD). PMID: 28035777
- This article aims to critically discuss the clinical and pathological features of Hailey-Hailey disease, differential diagnoses, and genetic and functional studies of the ATP2C1 gene in Hailey-Hailey disease. [review] PMID: 28551824
- review of the literature about the mutations occurring on the ATP2C1 gene and summarize how they are distributed along the gene and how missense mutations affect protein expression PMID: 27277681
- The Secretory Pathway Ca(2+) -ATPases SPCA1 and SPCA2 are strongly induced under osteogenic conditions that elicit microcalcifications. SPCA gene expression is significantly elevated in breast cancer subtypes that are associated with microcalcifications. PMID: 28618103
- xpressing either wild-type or mutant forms of SLC30A10 was sufficient to inhibit the effect of ATP2C1 in response to Mn challenge in both zebrafish embryos and HeLa cells. These findings suggest that either activating ATP2C1 or restoring the Mn-induced trafficking of ATP2C1 can reduce Mn accumulation, providing a possible target for treating HMDPC. PMID: 28692648
- SPCA1a is highly sensitive to the lipid environment and that several SERCA inhibitors, including thapsigargin (Tg), also block SPCA1a activity, although at higher concentrations only. There were differences in the relative contribution of Tg side chains in the inhibition of SERCA1a versus SPCA1a. PMID: 28264934
- A heterozygous deletion mutation, c. 2445_2454del 10bp, p.Cys814Leu fs*7, was detected in all three Hailey-Hailey disease subjects. This mutation has not yet been described. PMID: 26242806
- In this study, direct DNA sequencing was used to identify ATP2C1 gene mutations in four Chinese families and two sporadic cases with Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 27095120
- Two novel ATP2C1 mutations have been found in two unrelated Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease pedigree. PMID: 26782588
- we identified two causative genetic mutations responsible for Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 24981372
- Besides the level of functional ATP2C1 protein, levels of other ATPase proteins may influence expressivity of the disease and may also contribute to atypical presentations in three male members of the Hailey Hailey disease family. PMID: 25837627
- This is the first genetic report of HHD from Lebanon in which we identified three novel mutations in ATP2C1 and shed light on the molecular mechanisms and pathogenesis of HHD by linking stress signals like heat shock to the observed phenotypes PMID: 25658765
- We speculate that a novel pathogenic mechanism involving SPCA1, p63, and IRF6 may play a role in the skin lesions occurring in HHD. PMID: 25256005
- Data suggest that calcium ATPase ATP2C1 gene expression is influenced by an overlapping protein asteroid homolog 1 ASTE1 gene. PMID: 23344038
- The CFL-1-dependent recruitment of actin to SPCA1 following calcium influx is critical for secretory cargo sorting. PMID: 25179631
- Case Report: haploinsufficiency of ATP2C1 mutations is the causative mechanism of Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 23474827
- We report sibling cases of Hailey-Hailey disease with novel mutations in the ATP2C1 gene that showed unique and atypical clinical phenotypes mimicking seborrheic dermatitis, pemphigus vulgaris, or pemphigus foliaceus PMID: 24352221
- A novel mutation is identified in ATP2C1 linked to Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 23442470
- we report four novel mutations of the ATP2C1 gene involved in HHD, expanding the repertoire of ATP2C1 mutations underlying HHD. PMID: 22607350
- SPCA1 regulates the levels of claudins 1 and 4, but does not affect desmosomal protein levels in keratinocytes. PMID: 22639968
- Human PMR1 bound to c-Src, was tyrosine phosphorylated, sedimented on polysomes, and catalyzed the selective decay of a PMR1 substrate mRNA. Human PMR1 expression stimulated cell motility. PMID: 22543864
- genetic polymorphism is associated with Hailey-Hailey disease in Chinese patients PMID: 22124882
- we report five novel mutations and four recurrent mutations of the ATP2C1 gene in Chinese patients. This further expands the mutation spectrum in Hailey-Hailey Disease. PMID: 21883398
- The detection of an ATP2C1 gene mutation in this infant confirmed the diagnosis of Hailey Hailey disease PMID: 20403116
- The SPCA1 knockdown, like ADF/cofilin1 knockdown, inhibited Ca(2+) uptake into the TGN and caused missorting of secretory cargo. PMID: 21571222
- Correct SPCA1 functioning is crucial to intra-Golgi transport and maintenance of the Golgi ribbon. PMID: 20604898
- Heterogeneous mutations of the ATP2C1 gene cause Hailey-Hailey disease in Hong Kong Chinese. PMID: 20236194
- analysis of a gain-of-function mutation in a Golgi P-type ATPase that enhances Mn2+ efflux and protects against toxicity PMID: 21187401
- SPCA1 inhibites the processing of IGF1R in MDA-MB-231 cells. PMID: 20837466
- two specific novel mutations of the ATP2CL gene were identified two typical Chinese pedigrees with Hailey-Hailey disease PMID: 20055875
- SPCA1 is associated with cholesterol-rich domains of HT29 cells, and the cholesterol-rich environment is essential for the functioning of the pump PMID: 20363212
- Six novel ATP2C1 mutations are identified in Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 20226632
- failed to yield any clear correlation between the nature of the mutation and clinical features of Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 11841554
- Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) is caused by mutations in the ATP2C1 gene. PMID: 11966689
- the crucial role of Asp-742 in the architecture of the SPCA1 ion-binding site and a role of Gly-309 in Mn2+ transport selectivity. PMID: 12707275
- SPCA1 Ca2+ pump has a role in the Ca2+ accumulation in the Golgi apparatus of HeLa cells PMID: 12804581
- the abnormal Ca2+ signaling seen in Hailey-Hailey disease keratinocytes correlates with decreased protein levels of ATP2C1. PMID: 14632183
- Functional analyses of Hailey Hailey disease-mutant A528P demonstrated a low level of protein expression, despite normal levels of mRNA and correct targeting to the Golgi, suggesting instability or abnormal folding of the mutated hSPCA1 polypeptides PMID: 15191544
- A review of the role of SPCA1 in ion homeostasis in the golgi apparatus and in Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 15336968
- Two copies of mutated ATP2C1 were found in an index case diagnosed with type 2 segmental Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 15545997
- important contributions of the Golgi-localized ATP2C1 protein in homeostatic maintenance throughout the secretory pathway. PMID: 15623514
- Intracellular Ca(2+) stores and store-dependent [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations in human spermatozoa rely primarily on a thapsigargin/cyclopiazonic acid-insensitive Ca(2+) pump, SPCA1. PMID: 15811949
- Sp1 and YY1 transactivate human ATP2C1 promoter via cis-enhancing elements and that incomplete upregulation of ATP2C1 transcription contributes to keratinocyte-specific pathogenesis of Hailey-Hailey disease. PMID: 15955096
- Relative to SERCA1a, the active SPCA1a, SPCA1b, and SPCA1d enzymes displayed extremely high apparent affinities for cytosolic Ca(2+) in activation of the overall ATPase and phosphorylation activities. PMID: 16192278
- The high allelic heterogeneity of the ATP2C1 gene was confirmed, which supports the notion that Hailey-Hailey disease is a genetically homogeneous disorder. PMID: 16297192
- analysis of SPCA1 and SPCA2 isoenzymes by steady-state and transient kinetic analyses PMID: 16332677
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD)
-
亞細胞定位:Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus, Golgi stack membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Cation transport ATPase (P-type) (TC 3.A.3) family, Type IIA subfamily
-
組織特異性:Found in most tissues except colon, thymus, spleen and leukocytes. Expressed in keratinocytes (at protein level).
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-